1. Have the
Nutrition Honor.
The nutrition honor is required rather than duplicating activities about
proper nutrition. The digestion honor deals with how food is used by the
body.
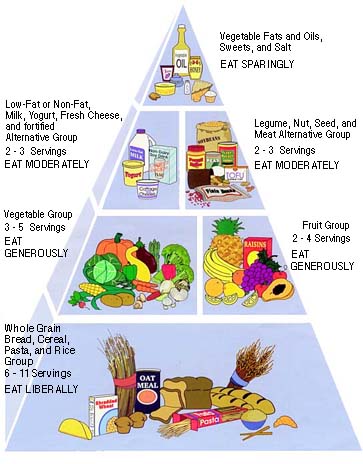
2. Keep a record of what and how much
food that you eat for two weeks. Compare your diet to that of the
food pyramid.
A simple daily chart can be made to compare
your records to the nutrition pyramid. Determine what food groups are
lacking or what you may have eaten and excess of.
3. What is digestion? What is another
name for the human digestive system?
Digestion is the process of breaking down food
into simpler/smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. The
other name for the human digestive system is the gastrointestinal tract of GI
tract.
4. Where does saliva come from? What
are the three functions of saliva?
Saliva comes from the salivary gland that is
located under the tongue. It is secreted into the mouth by little ducts
that are all over the mouth. The main functions of saliva are to:
1. Dissolve some foods and combines
with mucus to speed the passage of food through the digestive system.
2. Contain chemicals that attack many of the potentially dangerous
micro-organisms that can enter the body mouth.
3. Contain the enzyme salivary amylase, which breaks up long starch
molecules into shorter maltose molecules.
5. Be able to identify the following
parts of the tooth: dentin, cementum, periodontal membrane, enamel, pulp, and
gum. What role do the teeth play in digestion?
During the process of chewing teeth break the
food into smaller pieces and gets it ready to go into the stomach for further
digestion with the help of saliva.

6. Starting from where the food goes into the mouth
to where it is expelled from the anus, label a diagram or model of all the
organs that help with digestion.
Mouth, Pharynx, Esophagus, Sphincter muscle, Stomach,
Pyloric valve, *Liver, *Pancreas, *Gallbladder, Small intestine **(duodenum,
jejunum, and illium), Appendix, Cecum, Large intestine or colon **(ascending
colon, traversing colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon), Rectum, and
Anus. *these are accessory glands that secrete digestive juices into the
duodenum.
**these are the different names of parts of the small intestine and colon.
7. Know the difference between bolus and chyme.
Bolus is a ball of partially digested food formed in the mouth after the
initial digestive processes of the teeth and salivary glands have acted upon
it.
Chyme is a pasty mixture that results after food is
partially digested in the stomach.
8. Where does bile come from? Where is it
stored? and what does it do in the duodenum?
Bile is made in the liver and stored in the
gallbladder. When released into the duodenum it helps with the digestion of
fat.
9. What is villi?
Villi are miniature folds in the walls of the small intestine that
increase the surface area.
What makes them absorb the nutrients so quickly?
The villi in the small intestine are richly supplied with blood vessels
that quickly absorb and carry away the nutrients.
At what point are all the nutrients removed from the
food/chyme?
Chyme is basically nutrient free when it is ready to leave the small
intestine.
Compare the amount of water absorbed by plain paper
compared to a similar sized paper towel when using 1/8 cup of water.
Ball up a piece of plain paper and place it in 1/8 of a cup of water. Ball
up a piece of paper towel and place in another 1/8 cup of water. Remove
both pieces of paper and see which on absorbed more water. The paper
towel absorbs more water because it has miniature folds, just like our small
intestine.
10. What happens if too much water is present in
the large intestine? What happens if not enough water is present?
An excess of water in the large intestine results in diarrhea. The
lack of water in the large intestine results in constipation.
11. How does fiber in your diet aid in digestion?
How long should food remain in the digestive tract? What happens if food
stays in the digestive system too long?
Fiber absorbs excess fat and carries it out of the body in the waste
products. It also helps the food move along in the digestion process,
not letting it get clogged up during the removal from the body. Ideally
the digestive process should be completed in 30 hours or less. If food
does not move along fast enough, it can rot and make toxins that can cause
cancer.
12. Demonstrate the digestion of starch into a
simple sugar, using the iodine test.
Mix one teaspoon of cornstarch and one cup of warm water. Transfer
two tablespoons of this mixture into each individual's cup. Take two
drops of iodine (available at most drugstores) and add it to two drops of your
starch mixture on a Styrofoam plate. Notice the presence of starch
causes the iodine to turn purple. To start the digestion process, spit
two of three times into the cup and stir (chewing on your tongue for a few
seconds will increase the amount of saliva - remember saliva contains the
enzyme amylase which breaks down starch). After five minutes, test the
solution by adding two drops of the solution to tow drops of iodine in a
different spot on the plate. Compare the color to the original reaction
(one without saliva). Repeat this test every five minutes until the
purple reaction stops, which indicates that the starch has been completely
digested into simple sugar.
Hints:
1. Some peoples saliva may not have any enzyme.
2. The iodine should be diluted so it is light yellow in color.
3. Iodine reacts with cotton because cotton is a starch. So it
WILL stain clothes.
13. What are the six basic nutrients that are
essential for life and where does the bulk of their digestion/absorption take
place?
Carbohydrates - starts in the mouth and absorbed in the small intestine.
Fat - small intestine with the help of the liver and gall bladder.
Protein - stomach and small intestine with the help of the pancreas.
Vitamins - small intestine
Minerals - small intestine and large intestine
Water - large intestine
14. Know the difference between monosaccharide,
disaccharide, and polysaccharide. What is the most important carbohydrate?
Monosaccharide are simple sugars. Disaccharides are made from two
monosaccharides. Polysaccharides are long are long chains of
monosaccharides. All three of these are referred to as carbohydrates.
The most important of these is glucose, which is a monosaccharide.
15. What are amino acids?
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein.
How many are needed to make all the proteins in the body?
Twenty different types are needed to properly make all the proteins in the
body.
What is meant by essential amino acids?
Essential amino acids have to be eaten because your body cannot make them.
How many of them are essential?
Eight amino acids are essential.
Where can you get all the essential amino acids?
Eating corn (or other grains) and beans (or other legumes) will give you
the essential amino acids your body needs.
16. What is ATP?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is an energy molecule.
What is it used for?
ATP is used for everything your body does that requires energy.
What does your body make ATP from?
ATP is made from sugar, fat and protein that you eat.
What three sets of chemical reactions make ATP in your
body?
Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport
Why do we need to breathe oxygen?
Oxygen is needed to make ATP
17. Know the difference between water and fat
soluble vitamins. What are the two common vitamins that are fat soluble?
What are two vitamins that are water soluble?
Water soluble vitamins dissolve in water and do not stay in the body.
Fat soluble vitamins do not dissolve in water and are stored in fat in the
body.
Water soluble vitamins - C, Niacin, B12, Thiamine,
Riboflavin
Fat soluble vitamins - A, D, E, K
18. Give four Bible texts that refer to digestion.
Ezekiel 2:3 - Then he said to me, "Son of man, eat this
scroll I am giving you and fill your stomach with it." So I ate it, and it
tasted sweet as honey in my mouth.
Matthew 15:17 - "Don't you see that whatever enters the
mouth goes into the stomach the then out of the body?"
1 Corinthians 6:13 - "Food for the stomach and the stomach
for the food" - but God will destroy them both. The body is not meant
for sexual immorality; but for the Lord and the Lord for the body.
Proverbs 18:20 - From the fruit of his mouth a man's stomach
is filled; with the harvest from his lips he is satisfied.
19. Give five E.G. White references that promote
proper digestion. Goose a variety of topics.
COUNSELS ON DIET and FOOD
p. 50 lines: 8-12 - The sin of intemperate eating, eating too frequently, too
much, and of rich, unwholesome food, destroys the healthy action of the
digestive organs, affects the brain, and perverts the judgment, preventing
rational, calm, healthy think and acting.
p. 180 lines: 1-5 - Regularity in eating should be carefully
observed. Nothing should be eaten between meals, no confectionery, nuts,
fruits or food of any kind. Irregularities in eating destroy the
healthful tone of the digestive organs, to the detriment of health and
cheerfulness.
p. 199 lines: 13-20 - There are some who go to extremes.
They must eat just such an amount and just such a quality, and confine
themselves to two or three things. They allow only a few things to be
placed before them or their families to eat. In eating a small amount of food,
and that not of the best quality, they do not take into the stomach that which
will suitably nourish the system. Poor food cannot be converted into
good blood. An impoverished diet will impoverish the blood.
p. 236 lines: 14-18 - Flesh meats, butter, cheese, rich
pastry, spiced foods, and condiments are freely partaken of by both the old
and young, these things do their work in deranging the stomach, exciting the
nerves and enfeebling the intellect.
p. 328 lines: 16-22 - Anything that hinders the active
motion of the living machinery, affects the brain directly. And from the
light given me, sugar, when largely used, is more injurious than meat.
These changes should be made cautiously, and the subject should be treated in
a manner not calculated to digest and prejudice those whom we would teach and
help